To day I show you how to Access .NET Web service (K Soap Service) in android .
As you may know, we often want to access Web services via hand-held devices, and most likely you will run into trouble parsing the WSDL and the SOAP messages.
This is very Important topic by knowing this technique you can easily make Android application of you asp.net website ,web Application and web services.
Please follow the Following Steps:
First You have to Download the Ksoap assembly jar file and to include in Project .
First things first, so you should now go ahead and download the KSOAP library fromSourceforge Google code (*UPDATE* thanks Freddy):
http://code.google.com/p/ksoap2-android/downloads/detail?name=ksoap2-android-assembly-2.4-jar-with-dependencies.jar&can=2&q=
Then copy and paste the KSOAP library in the folder where your Android project will reside. Open Eclipse, start a new Android Project, right-click on the project's name and choose Properties, like this:
The next thing you need to do is to Add the KSOAP .JAR into the Android Project:
Go ahead an press Add JARs... button. Then navigate to the folder where your KSOAP library is and select it. Once you have this done, you are ready to start working with your Web Service library.
First, let's take a look at our web service call in Visual Studio:
When you open this webservice in browser, you can see a window like in the figure below:
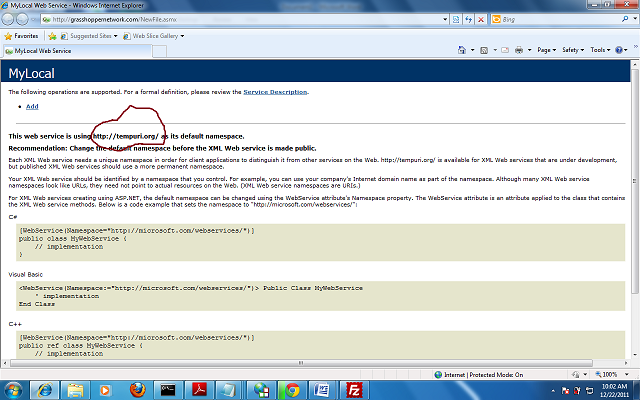
I have marked it to show how to get the namespace name. It will also show the list of methods, which you cannot test. So how to know the arguments and return type? Click on the method and see the figure below:
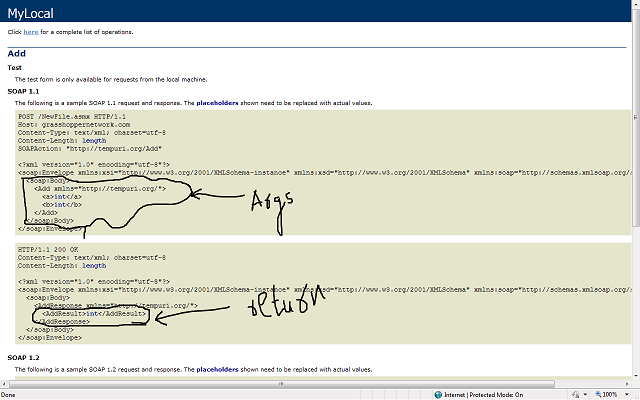
Now you know what function you are calling, its arguments, return type and namespace (and of course URL).
For calling this method you need
Copy the downloaded zip file in any appropriate location. This is an external jar file which you need to include in your Android project.
Start an Android project and select Android API. Right click on the project node in the workspace, properties->java build path->libraries->Add external jar.
Browse and select your ksoap jar file.
All we have to do now is to write a method which can call the web service and return the result. Remember that Android gives you an exception if you try any socket operation from main activity thread. Therefore it is better to write a separate class and isolate soap related functions.
Let us now understand the logic of this class.
Create a serialized envelope which will be used to carry the parameters for SOAP body and call the method through
Now you are very much ready with techniques for calling web method and getting the result. For simplicity, we have made a simple Android GUI with two
See the main.xml code as below:
Once you get this up and running, you are very much likely to get an error like
That is because Android does not permit you to run socket related operations from main thread as we had already discussed. So you need to run a thread or create a thread from where you can perform these operations. You can easily model the
But now the problem is your activity thread and the network thread are in multi-thread operation and chances are your main thread ends before getting the result from the SOAP operation. So I used a primitive way of waiting for the result to arrive and then using it.
The caller class.
Modified
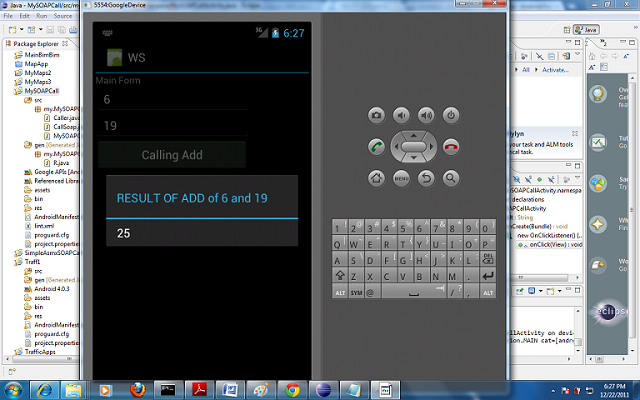
Finally you get the results as shown below:
DOWNLOAD SOURCE CODE OR DOWNLOAD SOURCE CODE (Recommended To Download)
As you may know, we often want to access Web services via hand-held devices, and most likely you will run into trouble parsing the WSDL and the SOAP messages.
This is very Important topic by knowing this technique you can easily make Android application of you asp.net website ,web Application and web services.
Please follow the Following Steps:
First You have to Download the Ksoap assembly jar file and to include in Project .
Getting Started with KSOAP on Android
First things first, so you should now go ahead and download the KSOAP library from
http://code.google.com/p/ksoap2-android/downloads/detail?name=ksoap2-android-assembly-2.4-jar-with-dependencies.jar&can=2&q=
Then copy and paste the KSOAP library in the folder where your Android project will reside. Open Eclipse, start a new Android Project, right-click on the project's name and choose Properties, like this:
The next thing you need to do is to Add the KSOAP .JAR into the Android Project:
Go ahead an press Add JARs... button. Then navigate to the folder where your KSOAP library is and select it. Once you have this done, you are ready to start working with your Web Service library.
Simple Web Service Calls with KSOAP
First, let's take a look at our web service call in Visual Studio:
[WebService(Namespace = "http://vladozver.org/")] public class SimpleWebServices : System.Web.Services.WebService { [WebMethod] public int GetSumOfTwoInts(int Operand1, int Operand2 ) { return Operand1 + Operand2; } }
The service is deployed on my local machine which is on the address: 192.168.1.3. Pay attention on the ending "/" in the Namespace.
So it mean when you access the web service you have to use your desktop machine
ip address like (192.168.1.3) instead of Local host.While creating this webservice, it asks for a namespace and here the namespace is www.tempura.org (pretty much the default namespace which I have not changed!). You can open this service from http://grasshoppernetwork.com/NewFile.asmx.
When you open this webservice in browser, you can see a window like in the figure below:

I have marked it to show how to get the namespace name. It will also show the list of methods, which you cannot test. So how to know the arguments and return type? Click on the method and see the figure below:

Now you know what function you are calling, its arguments, return type and namespace (and of course URL).
For calling this method you need
ksoap library, which you can download from here.Copy the downloaded zip file in any appropriate location. This is an external jar file which you need to include in your Android project.
Start an Android project and select Android API. Right click on the project node in the workspace, properties->java build path->libraries->Add external jar.
Browse and select your ksoap jar file.
All we have to do now is to write a method which can call the web service and return the result. Remember that Android gives you an exception if you try any socket operation from main activity thread. Therefore it is better to write a separate class and isolate soap related functions.
Let us now understand the logic of this class.
package my.MySOAPCallActivity.namespace; import org.ksoap2.SoapEnvelope; import org.ksoap2.serialization.PropertyInfo; import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject; import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapSerializationEnvelope; import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE; public class CallSoap { public final String SOAP_ACTION = "http://tempuri.org/Add"; public final String OPERATION_NAME = "Add"; public final String WSDL_TARGET_NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/"; public final String SOAP_ADDRESS = "http://grasshoppernetwork.com/NewFile.asmx"; public CallSoap() { } public String Call(int a,int b) { SoapObject request = new SoapObject(WSDL_TARGET_NAMESPACE,OPERATION_NAME); PropertyInfo pi=new PropertyInfo(); pi.setName("a"); pi.setValue(a); pi.setType(Integer.class); request.addProperty(pi); pi=new PropertyInfo(); pi.setName("b"); pi.setValue(b); pi.setType(Integer.class); request.addProperty(pi); SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope( SoapEnvelope.VER11); envelope.dotNet = true; envelope.setOutputSoapObject(request); HttpTransportSE httpTransport = new HttpTransportSE(SOAP_ADDRESS); Object response=null; try { httpTransport.call(SOAP_ACTION, envelope); response = envelope.getResponse(); } catch (Exception exception) { response=exception.toString(); } return response.toString(); } }
First
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(WSDL_TARGET_NAMESPACE,OPERATION_NAME);
SOAP_ACTION = namespace as seen in figure 1+function name; OPERATION_NAME = nameof the web method;WSDL_TARGET_NAMESPACE = namespaceof the webservice;SOAP_ADDRESS = absoluteURL of the webservice;
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(WSDL_TARGET_NAMESPACE,OPERATION_NAME);
Now the operation or the method that you intend to call has some arguments which you need to attach to the request object. This is done through
Using
PropertyInfo Instance pi. The important thing to notice here is that the name that you use in setName() method must be the exact name of the property that you have seen in the figure above and in setType(), the data type of the variable must be specified. Using addProperty(), add all the arguments.Using
setValue() method, set the value to the property.PropertyInfo pi=new PropertyInfo(); pi.setName("a"); pi.setValue(a); pi.setType(Integer.class); request.addProperty(pi);
Create a serialized envelope which will be used to carry the parameters for SOAP body and call the method through
HttpTransportSE method.Now you are very much ready with techniques for calling web method and getting the result. For simplicity, we have made a simple Android GUI with two
EditText and one Button.See the main.xml code as below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="230dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="232dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="229dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/btnStr" />
</LinearLayout> We want to call the method from button click event from
activity class. See the code below:package my.MySOAPCallActivity.namespace; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.AlertDialog; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; public class SimpleAsmxSOAPCallActivity extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); Button b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1); final AlertDialog ad=new AlertDialog.Builder(this).create(); b1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub CallSoap cs=new CallSoap(); try { EditText ed1=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1); EditText ed2=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2); int a=Integer.parseInt(ed1.getText().toString()); int b=Integer.parseInt(ed2.getText().toString()); ad.setTitle("OUTPUT OF ADD of "+a+" and "+b); String resp=cs.Call(a, b); ad.setMessage(resp); }catch(Exception ex) { ad.setTitle("Error!"); ad.setMessage(ex.toString()); } ad.show(); } }); } }
All you do now is get the values for
a and b from EditTexts and pass the values to call method. Call method returns the result of the web method.String resp=cs.Call(a, b);
ad.setMessage(resp);Once you get this up and running, you are very much likely to get an error like
android.os.NetworkOnMainThreadException. That is because Android does not permit you to run socket related operations from main thread as we had already discussed. So you need to run a thread or create a thread from where you can perform these operations. You can easily model the
CallSoap class as one implementing runnable and get the stuff. But I wanted to have the calling part as a separate entity. So I just made a separate thread class for calling the CallSoap method. It gives a nice layered implementation so that the thread that is calling the function where SOAP related activities are performed is completely different. But now the problem is your activity thread and the network thread are in multi-thread operation and chances are your main thread ends before getting the result from the SOAP operation. So I used a primitive way of waiting for the result to arrive and then using it.
The caller class.
public class Caller extends Thread { public CallSoap cs; public int a,b; public void run(){ try{ cs=new CallSoap(); String resp=cs.Call(a, b); MySOAPCallActivity.rslt=resp;}catch(Exception ex) {MySOAPCallActivity.rslt=ex.toString(); } } }
Modified
OnClick method of the button in activity thread which calls SOAP through this simple caller class.package my.MySOAPCallActivity.namespace; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.AlertDialog; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; public class MySOAPCallActivity extends Activity { public static String rslt=""; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); Button b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1); final AlertDialog ad=new AlertDialog.Builder(this).create(); b1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { EditText ed1=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1); EditText ed2=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2); int a=Integer.parseInt(ed1.getText().toString()); int b=Integer.parseInt(ed2.getText().toString()); rslt="START"; Caller c=new Caller(); c.a=a; c.b=b; c.ad=ad; c.join(); c.start(); while(rslt=="START") { try { Thread.sleep(10); }catch(Exception ex) { } } ad.setTitle("RESULT OF ADD of "+a+" and "+b); ad.setMessage(rslt); }catch(Exception ex) { ad.setTitle("Error!"); ad.setMessage(ex.toString()); } ad.show(); } }); } }
Finally you get the results as shown below:

DOWNLOAD SOURCE CODE OR DOWNLOAD SOURCE CODE (Recommended To Download)














0 comments:
Post a Comment